DM plant full form is Demineralization Plant. Demineralization is the process of eliminating mineral salts from water using the ion exchange method. Demineralization can be used with the majority of natural water sources to create water of a higher quality than that derived through traditional distillation.
Demineralized water is water that has been stripped of all dissolved minerals (or nearly so) as a result of one of the following processes:
- Distillation
- Deionization
- Filtration using membranes (reverse osmosis or nanofiltration)
- Electrodialysis
- Alternatively, there are other technologies.
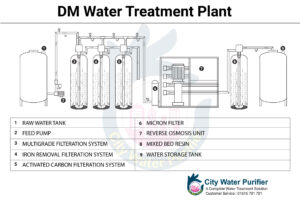
Water that has had its mineral ions removed, also known as Demineralized Water or Deionized Water. Mineral ions such as sodium, calcium, iron, copper, and others, as well as anions such as chloride, sulfate, and nitrate, are common ions found in water. Deionization is a physical process that involves the use of specially made ion exchange resins to offer an ion exchange site for the replacement of mineral salts in water with water, resulting in the formation of H+ and OH- ions. Deionization provides high purity water that is generally similar to distilled water, and the process is rapid and without scale formation because the bulk of Water contaminants are dissolved salts.
De-mineralization technology is a tried-and-true method of water treatment. A DM Water System works on the principles of ion exchange, degasification, and polishing to provide mineral-free water. In the fields of steam, power, process, and cooling, the Demineralized (DM) Water System is widely used.
Principal of Demineralised Water Plant
Two tiny polystyrene bead-filled (ion exchange resins) beds traverse raw water. The anions are swapped with hydroxyl ions in the second bed, while the cations are exchanged with hydrogen ions in the first.
DM Plant Process
Ion exchange, in the context of water purification, is a quick and reversible process in which contaminant ions in the water are replaced by ions released by an ion-exchange resin. The impurity ions are absorbed by the resin, which must be renewed on a regular basis to return to its original ionic state. (An ion is an electric-charged atom or group of atoms.) Cations are positively charged ions that are usually metals; anions are negatively charged ions that are usually non-metals).
In raw water, the following ions are commonly found:
Cations
- Calcium (Ca2+)
- Magnesium (Mg2+)
- Sodium (Na+)
- Potassium (K+)
Anions
- Chloride (Cl-)
- Bicarbonate (HCO3-)
- Nitrate (NO3-)
- Carbonate (CO32-)
Iron Exchange Resigns
Cation-exchange and anion-exchange resins are the two most common forms of resin. In exchange for impurity cations present in the water, cation exchange resins will release hydrogen (H+) ions or other positively charged ions. In exchange for impurity anions present in the water, anion exchange resins will release hydroxyl (OH-) ions or other negatively charged ions.
The use of ion-exchange technology in the treatment and purification of water. Ion-exchange technology can be applied to water treatment and purification in three ways:
First, cation-exchange resins can be used to soften water through a base exchange; second, anion-exchange resins can be used for organic scavenging or nitrate removal; and third, a combination of cation-exchange and anion-exchange resins can be used to deionize water by removing virtually all ionic impurities. The purifying process of water deionizers produces extremely high-quality water.
Deionization
High-purity Many laboratory and industrial applications demand water that is virtually free of ionic contaminants. This type of water can be made by deionization. The two most common types of deionization are as follows:
- Two beds with deionization
- In a mixed bed, deionization
Two-bed Deionization
The two-bed deionizer consists of two containers, one of which contains a hydrogen (H+) cation-exchange resin and the other of which contains an anion resin in the hydroxyl (OH-) form. All of the cations are exchanged for hydrogen ions as water travels through the cation column. To keep the water electrically balanced, one hydrogen ion is exchanged for every monovalent cation, such as Na+, and two hydrogen ions are exchanged for every divalent cation, such as Ca2+ or Mg2+. When it comes to anion exchange, the same idea applies. After that, the deionized Water passes via the anion column. All of the negatively charged ions are now swapped for hydroxide ions, which mix with the hydrogen ions to produce water (H2O).
Mixed-bed Deionization
Cation-exchange and anion-exchange resins are intimately combined and held in a single pressure vessel in mixed-bed deionizers. A mixed-bed deionizer is equal to a long sequence of two-bed plants due to the full mixing of cation-exchangers and anion-exchangers in a single column. As a result, the water quality produced by a mixed-bed deionizer is significantly superior to that of a two-bed machine. Mixed-bed plants are more sensitive to pollutants in the water supply and have a more difficult regeneration process, although being more efficient at purifying the incoming feedwater. After the water has been treated by either a two-bed deionizer or a reverse osmosis unit, mixed-bed deionizers are typically used to ‘polish’ it to greater degrees of purity.
Electro Deionization EDI
Typically used in conjunction with reverse osmosis (RO) and other purification equipment, electro deionization systems remove ions from aqueous streams. Our high-quality deionization modules produce ultrapure water up to 18.2MW/cm on a continuous basis. EDI can be used on a continuous or intermittent basis.
Advantages of DM Water Plant
- Standard versions in a variety of price ranges.
- Aesthetics have been improved, and the design has been made more durable.
- It’s user-friendly, low-maintenance, and simple to set up.
- Distribution and collecting systems that are less complicated.
- The quick availability is a plus.
- Check the assembly before sending it off.
- The multiport valves can be positioned on the top or on the side, with the requisite high-pressure PVC piping.
- In contrast to typical filters, which have six valves, one valve operation is possible.
- Each operational phase is clearly defined on the valve, removing the possibility of an error in the sequence.
- With its streamlined frontal piping and simpler distribution collecting systems, the single valve assembly is very simple to install.
- Free of rust
- Power usage is reduced.
- Durable
- Economical
- a long shelf life
Learn More: Overview Of Demineralization Water Therapy Vegetation
Major Applications of DM Water Treatment Plant
- Water, Textiles, Pharmaceuticals, Chemicals, Breweries, Swimming Pools, Potable Water, Hospitals, Automobiles, and Fertilizers are all served by boilers.
- Plants that exchange ions
– Softener
– Industrial DM Plants
– Two and Multi-Stage DM Plants
– Mix Bed Demineralizer
– Degasifies
– Cation Polishers
– Manual and Automatic Plants
– Pharmaceutical Industry
– Power plants
– Oil and gas industries
– Chemical and textile industries
We Offer
Our organization provides a high-quality DM water Plant that is made with cutting-edge technology. Our company’s Demineralization Water Treatment Plant is in high demand in a variety of industries and municipal sectors. We are now known as one of the most reliable Demineralization Water Plant providers.
Portable o Mini–DM Water Treatment Plant
De-mineralized water is water that is devoid of minerals (D.M.Water). The dissolved solids (TDS) in naturally occurring water are a mixture of salts in a dilute state. When water containing such a mineral needs to be purified, it is passed through an Ion Exchange Resins column (H form) that adsorbs the positively charged ion. Now the free cations travel through an anion resin column (OH form) that adsorbs the negatively charged anions, and the total ions are separated from the water.
Mini DM Plant Specifications
- eDM-5 is the model number.
- Flow rate: 50-80 liters per hour
- 1 m x 1 m is the minimum space necessary.
- NIL power, 0.5 kg/cm2 minimum inlet pressure
- TDS in the output: less than 10 ppm
- DM output Qty.: 500 Lit at 100 ppm TDS (Best when feed water has a TDS of less than 100 ppm)

